What Are the Differences Between Regular and Thermoelectric Separation Copper-Base PCBs?
- Views
- 15 Apr 2024
Printed circuit boards (PCBs) have become a necessary part of electronics, especially for the rapid development of the 5G communication and AI era. However, as devices gradually to powerful and compact, managing the heat they generate becomes a paramount concern. Then led to the development of specialized PCBs, among which metal core PCBs, particularly those with copper bases, have gained prominence for their thermal management capabilities. This blog delves into the researches of regular and thermoelectric separation copper-base PCBs, shedding light on their differences and guiding you in selecting the appropriate PCB for your devices.

Why Do We Need Metal Core PCBs for Thermal Management?
At the beginning, we should know why the metal core PCBs win the market and how does it work for our devices. Actually, the core purpose of metal core PCBs is to efficiently dissipate heat away from critical components of electronic devices, preventing overheating and ensuring reliability and longevity of the products. Traditional fiberglass-based PCBs are not as efficient in handling the heat generated by today's high-performance electronic components.
Metal core PCBs, especially those made with copper, offer superior thermal conductivity. That’s why they often be used in high-power applications, such as LED lighting, automotive systems, and power supplies, where effective heat dissipation is crucial for performance and safety. From a professional perspective, copper substrate PCB always has better thermal management and mechanical performance than other metal materials.
What are the advantages using copper as PCB core instead of other metal materials?
According to the different materials, the PCB metal substrate on the market is mainly involves three types: aluminum, copper and iron substrate. Among them, the circuit board made of copper substrate has the most advantages.
1. Thermal conductivity
Firstly, the thermal conductivity of copper-based materials is several times higher than that of aluminum-based and iron-based materials. Aluminum PCB has 1-3W/m.k thermal conductivity while copper-based PCB can reach up to 400W/m.k (depends on the used technology). It's important to understand that the higher the thermal conductivity, the higher the heat conduction power, and thus, the better the cooling function. Moreover, copper materials have a high density and strong heat carrying capacity, allowing for a smaller volume under the same power conditions.
2. Metalized holes available
Copper-based boards can be processed to include metalized holes, while aluminum-based and iron-based boards cannot. During the PCB design, the network of metalized holes must be uniform to ensure good grounding performance for signals. Additionally, copper material itself is solderable, allowing for the option of soldering in the assembly process. Of course, aluminum PCB can be soldered as well, but the solderability is not so good than copper.
3. Enable to create convexity on copper surface
This is special point that copper-based boards can be etched to create precise patterns and processed into individual convexities, so the LED chips can be directly mounted on these convexities, achieving superior grounding and cooling effects. This kind of copper PCB we call it as SinkPad PCB or thermoelectric separation copper PCB.
4. Excellent dimension stability
Due to the significant difference in the elastic modulus between copper (approximately 121,000MPa) and aluminum (72,000MPa), copper-based boards exhibit less warping and expansion than aluminum-based and iron-based boards, resulting in overall more stable functionality.
What are differences between normal copper core PCB and thermoelectric separation copper PCB?
The primary distinction between a regular copper core PCB and a SinkPad PCB lies in their approach to managing heat. Both types use copper due to its excellent thermal and electrical conductivity, but their construction and heat dissipation mechanisms differ significantly. We will look at this more below.
Normal Copper Core PCB
Regular copper-based PCBs are essentially PCBs with a solid copper core. They facilitate heat dissipation through this core, which acts as a thermal bridge between the hot components and the cooler parts of the board or the external heat sink. The copper core spreads the heat evenly across the PCB, reducing hotspots that can damage sensitive components. The normal copper PCB always consist of three layers – metal layer, dielectric layer and a circuit layer on the top. Due to the metal core circuit boards are always used in LED applications, let’s take a simple example with LED chips.
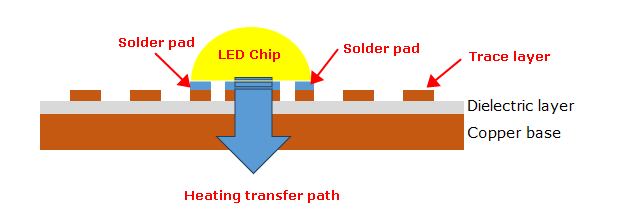
As you can see from the above structure, when a LED be mounted on the copper core PCB, heat generated by the LED is efficiently transferred from the dielectric layer to the copper base. So, the thermal conductivity of the dielectric material plays a crucial role in determining the overall heat dissipation efficiency of the PCB. And generally, the thermal conductivity of a dielectric material always not very high, commonly used are 1W, 2W and 3W.
Thermoelectric Separation Copper-Base PCBs
On the other hand, Sinkpad PCB employs a more advanced technique. They are designed with a special separation layer (BT/fr4) and convexity. The BT/FR4 material isolates the copper base from the electrical circuits while convexity can directly connect with the LED chips. This layer serves two purposes: it allows for efficient thermal transfer from the components to the copper base and, crucially, reduces the thermal stress on the electrical circuits. This separation not only enhances the PCB's ability to dissipate heat but also minimizes the thermal impact on the electronic components, improving the device's overall performance and durability. Below is a diagram shows how does the thermoelectric separation PCB dissipate the heat.
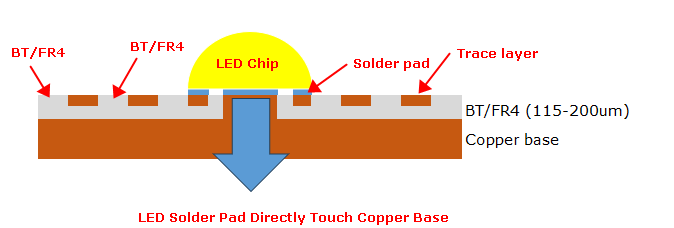
With this convexity, the heat generated by LED can be directly transfer to copper base, then transfer the heat out by the copper base. This is why the thermal conductivity of thermoelectric separation copper core PCB can be achieved to 400W/m.k
How to Select a Suitable PCB for Your Device?
Selecting the right PCB for your device involves considering several factors, including the device's power consumption, the environment in which it will operate, and the physical space available for the PCB. For applications that generate a significant amount of heat or are sensitive to temperature fluctuations, a thermoelectric separation copper-base PCB is often the better choice. Its superior thermal management capabilities ensure that the device operates within safe temperature ranges, even under high load.
However, for devices with moderate heat generation or where cost is a major consideration, a regular copper core PCB might be sufficient. It still offers better heat dissipation than non-metal core PCBs and can be a cost-effective solution for many applications.
Words In the End
The choice between a regular copper core PCB and a thermoelectric separation copper-base PCB boils down to the specific needs of your electronic device. While both types offer enhanced thermal management compared to traditional PCBs, the advanced technology of thermoelectric separation provides superior protection against thermal stress, making it suitable for high-performance and high-reliability applications. Understanding the differences between these PCBs allows designers and engineers to make informed decisions, ensuring that their devices not only meet but exceed performance and reliability expectations. As technology continues to advance, the importance of selecting the right PCB for thermal management will only grow, underlining the need for continued innovation and adaptation in PCB design and manufacturing.
copper core pcb, copper based pcb, copper pcb, thermoelectric copper pcb, thermoelectric separation copper pcb, sink pad pcb, aluminum pcb, led pcb, mcpcb, metal core pcb,
Related Blog
- What is Thermal and Electrical Separating Pad in Metal Core PCB?
- LED PCB Assembly Process: Step-by-Step Guide for Beginners
- Why Always Recommend White Solder Mask Black Silkscreen for Aluminum PCB?
- What Materials Are Commonly Used for Manufacturing Lighting PCBs?
- Everything You Should Know About Metal Core Circuit Board
- What Are the Differences Between Ceramic PCB, Metal Core PCB And Standard FR4 PCB?
- Why Choose Best Technology As Your MCPCB Manufacturer?
- What is LED Light Circuit Board and How to Make it?
- When is International Labour Day in 2024 and What are the Significances of It?
- How Does A Convexity Comes Out On Thermoelectric Separation Copper Based PCB?
- Why is Aluminum LED PCB Important for Indoor Growth Lights?
- Application of Metal Core Pcbs in the Development of LED Technology
- Why Choose White Solder Mask for Metal core PCB When Used In LED Devices?
- Understanding Aluminum LED PCBs in 1000w LED Grow Lights
- What Are the Advantages of Metal Core PCB? How to Choose?
- Automotive Light Copper Core Pcb Production Process—testing
- Why Are Metal Core PCBs, Especially Copper Core, Used In Heat-Sensitive Electronics?
- How do aluminum LED PCBs improve LED efficiency?
- What Are the Differences Between Regular and Thermoelectric Separation Copper-Base PCBs?
- Aluminum PCB VS FR-4 Performance Comparison



